Progesterone Transdermal Patch
Estrogen Healthy. M Keygen. Women. Share on Overview. What Is It Estrogen refers to a group of hormones that play an essential role in the growth and development of female sexual characteristics and the reproductive process. Estrogen is probably the most widely known and discussed of all hormones. The term estrogen actually refers to any of a group of chemically similar hormones estrogenic hormones are sometimes mistakenly referred to as exclusively female hormones when in fact both men and women produce them. However, the role estrogen plays in men is not entirely clear. To understand the roles estrogens play in women, it is important to understand something about hormones in general. A contraceptive patch, also known as the patch, is a transdermal patch applied to the skin that releases synthetic estrogen and progestin hormones to prevent pregnancy. Progesterone Transdermal Patch' title='Progesterone Transdermal Patch' />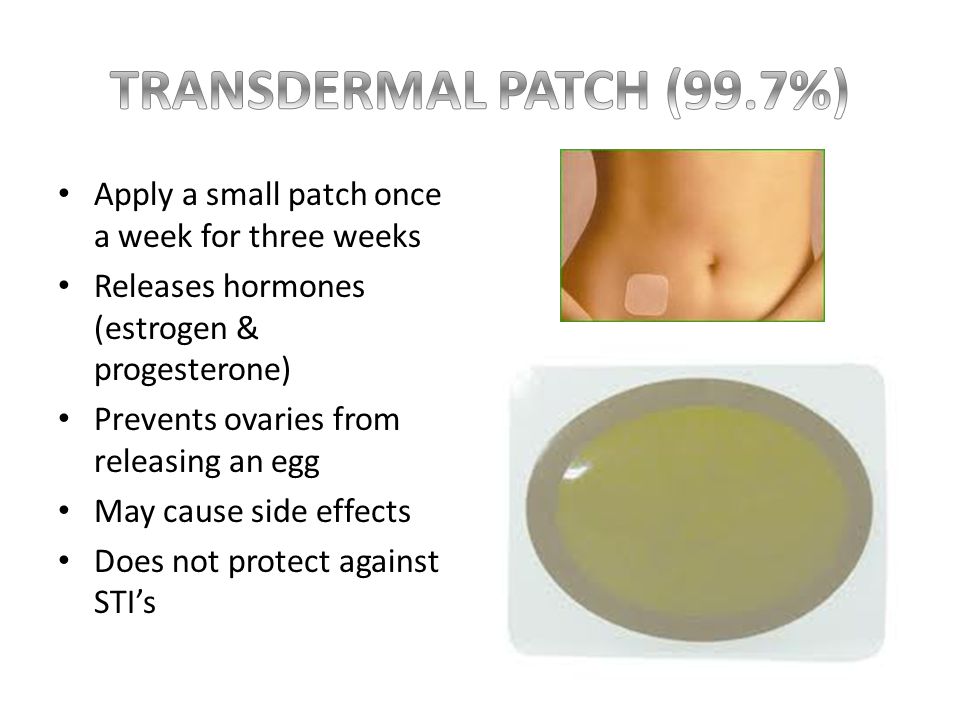 Hormones are vital chemical substances in humans and animals. Often referred to as chemical messengers, hormones carry information and instructions from one group of cells to another. In the human body, hormones influence almost every cell, organ and function. They regulate our growth, development, metabolism, tissue function, sexual function, reproduction, the way our bodies use food, the reaction of our bodies to emergencies and even our moods. The Role of Estrogen in Women. The estrogenic hormones are uniquely responsible for the growth and development of female sexual characteristics and reproduction in both humans and animals. Progesterone Transdermal Patch' title='Progesterone Transdermal Patch' />
Hormones are vital chemical substances in humans and animals. Often referred to as chemical messengers, hormones carry information and instructions from one group of cells to another. In the human body, hormones influence almost every cell, organ and function. They regulate our growth, development, metabolism, tissue function, sexual function, reproduction, the way our bodies use food, the reaction of our bodies to emergencies and even our moods. The Role of Estrogen in Women. The estrogenic hormones are uniquely responsible for the growth and development of female sexual characteristics and reproduction in both humans and animals. Progesterone Transdermal Patch' title='Progesterone Transdermal Patch' /> The term estrogen includes a group of chemically similar hormones estrone, estradiol the most abundant in women of reproductive age and estriol. Overall, estrogen is produced in the ovaries, adrenal glands and fat tissues. More specifically, the estradiol and estrone forms are produced primarily in the ovaries in premenopausal women, while estriol is produced by the placenta during pregnancy. Read about hormonal birth control methods, such as oral contraceptives, the patch, birth control injection, and vaginal ring and their side effects like nausea. In women, estrogen circulates in the bloodstream and binds to estrogen receptors on cells in targeted tissues, affecting not only the breasts and uterus, but also the brain, bone, liver, heart and other tissues. Estrogen controls growth of the uterine lining during the first part of the menstrual cycle, causes changes in the breasts during adolescence and pregnancy and regulates various other metabolic processes, including bone growth and cholesterol levels. Estrogen Pregnancy. During the reproductive years, the pituitary gland in the brain generates hormones that cause a new egg to be released from its follicle each month. As the follicle develops, it produces estrogen, which causes the lining of the uterus to thicken. Progesterone production increases after ovulation in the middle of a womans cycle to prepare the lining to receive and nourish a fertilized egg so it can develop into a fetus. If fertilization does not occur, estrogen and progesterone levels drop sharply, the lining of the uterus breaks down and menstruation occurs. If fertilization does occur, estrogen and progesterone work together to prevent additional ovulation during pregnancy. Birth control pills oral contraceptives take advantage of this effect by regulating hormone levels. They also result in the production of a very thin uterine lining, called the endometrium, which is unreceptive to a fertilized egg. Plus, they thicken the cervical mucus to prevent sperm from entering the cervix and fertilizing an egg. Oral contraceptives containing estrogen may also relieve menstrual cramps and some perimenopausal symptoms and regulate menstrual cycles in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome PCOS. Furthermore, research indicates that birth control pills may reduce the risk of ovarian, uterine and colorectal cancer. Other Roles of Estrogen. Bone. Estrogen produced by the ovaries helps prevent bone loss and works together with calcium, vitamin D and other hormones and minerals to build bones. Osteoporosis occurs when bones become too weak and brittle to support normal activities. Your body constantly builds and remodels bone through a process called resorption and deposition. Up until around age 3. But once estrogen levels start to decline, this process slows. Thus, after menopause your body breaks down more bone than it rebuilds. In the years immediately after menopause, women may lose as much as 2. Although the rate of bone loss eventually levels off after menopause, keeping bone structures strong and healthy to prevent osteoporosis becomes more of a challenge. Vagina and Urinary Tract. When estrogen levels are low, as in menopause, the vagina can become drier and the vaginal walls thinner, making sex painful. Additionally, the lining of the urethra, the tube that brings urine from the bladder to the outside of the body, thins. A small number of women may experience an increase in urinary tract infections UTIs that can be improved with the use of vaginal estrogen therapy. Perimenopause The Menopause Transition. Other physical and emotional changes are associated with fluctuating estrogen levels during the transition to menopause, called perimenopause. This phase typically lasts two to eight years. Estrogen levels may continue to fluctuate in the year after menopause. Symptoms include Hot flashesa sudden sensation of heat in your face, neck and chest that may cause you to sweat profusely, increase your pulse rate and make you feel dizzy or nauseous. A hot flash typically lasts about three to six minutes, although the sensation can last longer and may disrupt sleep when it occurs at night. Irregular menstrual cycles Breast tenderness Exacerbation of migraines Mood swings. Estrogen Therapy. Estrogen therapy is used to treat certain conditions, such as delayed onset of puberty and menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes and symptomatic vaginal atrophy. Vaginal atrophy is a condition in which low estrogen levels cause a womans vagina to narrow, lose flexibility and take longer to lubricate. Female hypogonadism, a condition in which the ovaries produce little or no hormones, as well as premature ovarian failure, can also cause vaginal dryness, breast atrophy and lower sex drive and is also treated with estrogen. For many years, estrogen therapy and estrogen progestin therapy were prescribed to treat menopausal symptoms, to prevent osteoporosis and to improve womens overall health. However, after publication of results from the Womens Health Initiative WHI in 2. March 2. 00. 4, the U. S. Food and Drug Administration FDA now advises health care professionals to prescribe menopausal hormone therapies at the lowest possible dose and for the shortest possible length of time to achieve treatment goals. Treatment is generally reserved for management of menopausal symptoms rather than prevention of chronic disease. The WHI was a study of 2. They were followed for an average of five and a half to seven years. The study was unable to document that benefits outweighed risks when hormone therapy was used as preventive therapy, and it found that risk due to hormones may differ depending on a womans age or years since menopause. The National Cancer Institute found a very significant drop in the rate of hormone dependent breast cancers among women, the most common breast cancer, in 2. In a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine in April 2. The researchers found that the decrease in breast cancer began in mid 2. The decrease occurred in women over 5. ER positivecancers that require estrogen to grow. The researchers speculate that stopping the treatment prevented very tiny ER positive cancers from growing and in some cases, possibly helped them to regress because they didnt have the additional estrogen required to fuel their growth. Things You Probably Dont Know About Birth Control. For every 1. 00 couples that use withdrawal as their birth control method, commonly known as the pull out method, four will become pregnant if they ALWAYS do it correctly, and 2. DONT ALWAYS do it correctly, according to a paper published in the June 2. Contraception magazine. The authors concluded that typical use of withdrawal leads to pregnancy 1. In comparison, for every 1. Those arent bad numbers for a free, all natural birth control method with zero side effects. But remember, withdrawal wont protect you from STDs, and couples rarely employ the withdrawal method 1. That means, if you plan on being sexually active, youre better off going with a more consistent, reliable form of birth control like the pill or an IUD. Related Signs Your Partner Is Having an Emotional Affair.
The term estrogen includes a group of chemically similar hormones estrone, estradiol the most abundant in women of reproductive age and estriol. Overall, estrogen is produced in the ovaries, adrenal glands and fat tissues. More specifically, the estradiol and estrone forms are produced primarily in the ovaries in premenopausal women, while estriol is produced by the placenta during pregnancy. Read about hormonal birth control methods, such as oral contraceptives, the patch, birth control injection, and vaginal ring and their side effects like nausea. In women, estrogen circulates in the bloodstream and binds to estrogen receptors on cells in targeted tissues, affecting not only the breasts and uterus, but also the brain, bone, liver, heart and other tissues. Estrogen controls growth of the uterine lining during the first part of the menstrual cycle, causes changes in the breasts during adolescence and pregnancy and regulates various other metabolic processes, including bone growth and cholesterol levels. Estrogen Pregnancy. During the reproductive years, the pituitary gland in the brain generates hormones that cause a new egg to be released from its follicle each month. As the follicle develops, it produces estrogen, which causes the lining of the uterus to thicken. Progesterone production increases after ovulation in the middle of a womans cycle to prepare the lining to receive and nourish a fertilized egg so it can develop into a fetus. If fertilization does not occur, estrogen and progesterone levels drop sharply, the lining of the uterus breaks down and menstruation occurs. If fertilization does occur, estrogen and progesterone work together to prevent additional ovulation during pregnancy. Birth control pills oral contraceptives take advantage of this effect by regulating hormone levels. They also result in the production of a very thin uterine lining, called the endometrium, which is unreceptive to a fertilized egg. Plus, they thicken the cervical mucus to prevent sperm from entering the cervix and fertilizing an egg. Oral contraceptives containing estrogen may also relieve menstrual cramps and some perimenopausal symptoms and regulate menstrual cycles in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome PCOS. Furthermore, research indicates that birth control pills may reduce the risk of ovarian, uterine and colorectal cancer. Other Roles of Estrogen. Bone. Estrogen produced by the ovaries helps prevent bone loss and works together with calcium, vitamin D and other hormones and minerals to build bones. Osteoporosis occurs when bones become too weak and brittle to support normal activities. Your body constantly builds and remodels bone through a process called resorption and deposition. Up until around age 3. But once estrogen levels start to decline, this process slows. Thus, after menopause your body breaks down more bone than it rebuilds. In the years immediately after menopause, women may lose as much as 2. Although the rate of bone loss eventually levels off after menopause, keeping bone structures strong and healthy to prevent osteoporosis becomes more of a challenge. Vagina and Urinary Tract. When estrogen levels are low, as in menopause, the vagina can become drier and the vaginal walls thinner, making sex painful. Additionally, the lining of the urethra, the tube that brings urine from the bladder to the outside of the body, thins. A small number of women may experience an increase in urinary tract infections UTIs that can be improved with the use of vaginal estrogen therapy. Perimenopause The Menopause Transition. Other physical and emotional changes are associated with fluctuating estrogen levels during the transition to menopause, called perimenopause. This phase typically lasts two to eight years. Estrogen levels may continue to fluctuate in the year after menopause. Symptoms include Hot flashesa sudden sensation of heat in your face, neck and chest that may cause you to sweat profusely, increase your pulse rate and make you feel dizzy or nauseous. A hot flash typically lasts about three to six minutes, although the sensation can last longer and may disrupt sleep when it occurs at night. Irregular menstrual cycles Breast tenderness Exacerbation of migraines Mood swings. Estrogen Therapy. Estrogen therapy is used to treat certain conditions, such as delayed onset of puberty and menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes and symptomatic vaginal atrophy. Vaginal atrophy is a condition in which low estrogen levels cause a womans vagina to narrow, lose flexibility and take longer to lubricate. Female hypogonadism, a condition in which the ovaries produce little or no hormones, as well as premature ovarian failure, can also cause vaginal dryness, breast atrophy and lower sex drive and is also treated with estrogen. For many years, estrogen therapy and estrogen progestin therapy were prescribed to treat menopausal symptoms, to prevent osteoporosis and to improve womens overall health. However, after publication of results from the Womens Health Initiative WHI in 2. March 2. 00. 4, the U. S. Food and Drug Administration FDA now advises health care professionals to prescribe menopausal hormone therapies at the lowest possible dose and for the shortest possible length of time to achieve treatment goals. Treatment is generally reserved for management of menopausal symptoms rather than prevention of chronic disease. The WHI was a study of 2. They were followed for an average of five and a half to seven years. The study was unable to document that benefits outweighed risks when hormone therapy was used as preventive therapy, and it found that risk due to hormones may differ depending on a womans age or years since menopause. The National Cancer Institute found a very significant drop in the rate of hormone dependent breast cancers among women, the most common breast cancer, in 2. In a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine in April 2. The researchers found that the decrease in breast cancer began in mid 2. The decrease occurred in women over 5. ER positivecancers that require estrogen to grow. The researchers speculate that stopping the treatment prevented very tiny ER positive cancers from growing and in some cases, possibly helped them to regress because they didnt have the additional estrogen required to fuel their growth. Things You Probably Dont Know About Birth Control. For every 1. 00 couples that use withdrawal as their birth control method, commonly known as the pull out method, four will become pregnant if they ALWAYS do it correctly, and 2. DONT ALWAYS do it correctly, according to a paper published in the June 2. Contraception magazine. The authors concluded that typical use of withdrawal leads to pregnancy 1. In comparison, for every 1. Those arent bad numbers for a free, all natural birth control method with zero side effects. But remember, withdrawal wont protect you from STDs, and couples rarely employ the withdrawal method 1. That means, if you plan on being sexually active, youre better off going with a more consistent, reliable form of birth control like the pill or an IUD. Related Signs Your Partner Is Having an Emotional Affair.